package section1;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class code03 {
static Person1 members[]= new Person1[100];
static int n = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Scanner in = new Scanner(new File("data.txt"));
while(in.hasNext()) {
String name = in.next();
String number = in.next();
members[n] = new Person1();
members[n].name=name;
members[n].number=number;
n++;
}
in.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("No file");
}
bubleSort();
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
System.out.println(members[i].name + " "+ members[i].number);
}
}
private static void bubleSort() {
for(int i=n-1;i>0;i--) {
for(int j =0; j<i; j++) {
if(members[j].name.compareTo(members[j+1].name) > 0 ) {
Person1 tmp = members[j];
members[j] = members[j+1];
members[j+1] = tmp;
}
}
}
}
}
저번시간의 코드를 살짝수정하여 버블정렬하는 코드를 작성했다
클래스를 사용하기 전에는 정렬시에 이름따로 번호따로 정렬을 하는 코드를 짰었는데
클래스를 사용하니 객체배열 각각의 참조변수에 주소값을 바꿔주어 이용하여 관련있는
데이터를 한번에 가르키게 될 수 있게 되엇다.
new명령어로 만들게 되면 고유한 이름을 가질 수 없기때문에
객체만 있어서는 객체를 사용할 수 없다 그래서 참조 변수가 필요하다
클래스, 참조변수, 객체에 대한 이해가 잘 되게 되었다!
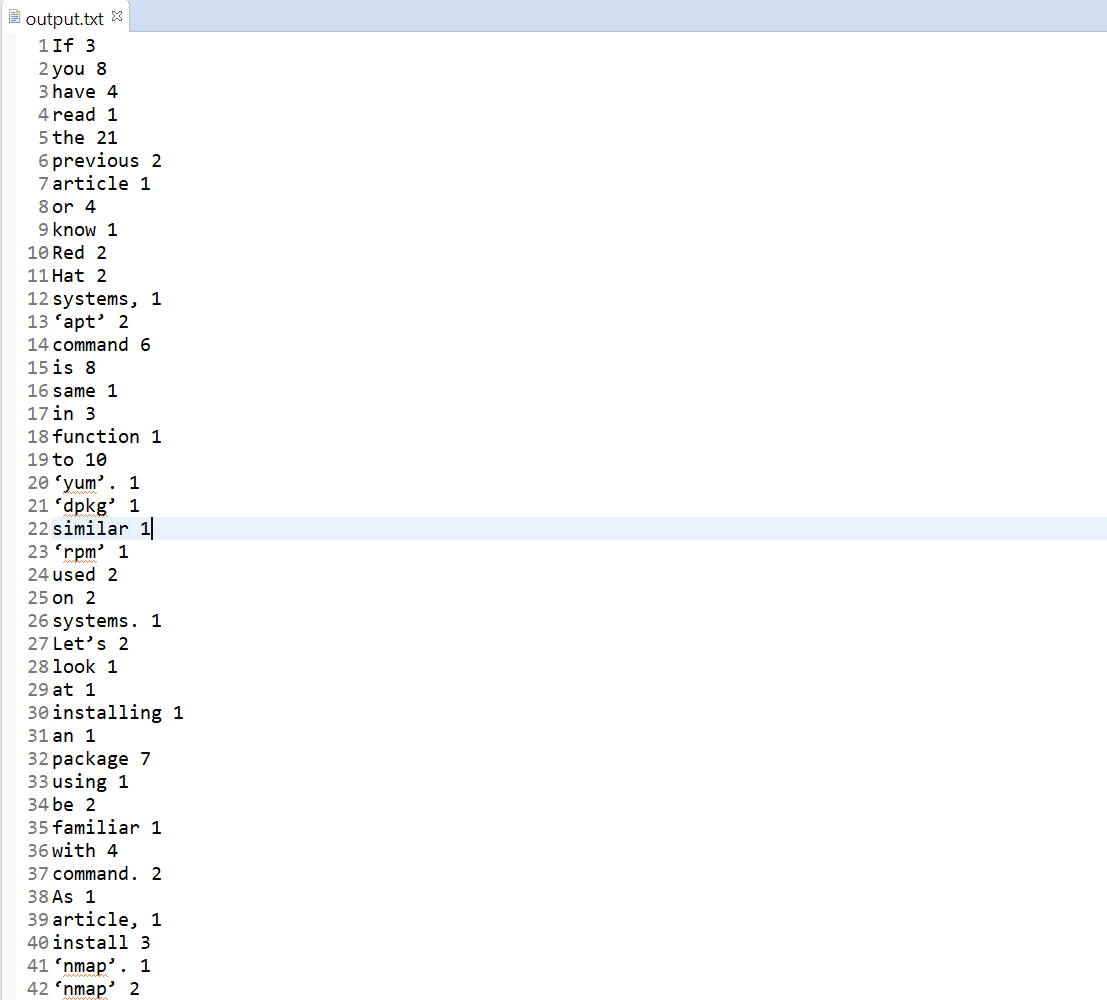
인덱스 메이커 프로그램의 수정
어떠한 텍스트 파일이 있다면 그 파일안에의 단어추출과 단어의 등장 빈도를 구해주는 프로그램을
클래스를 사용하여 리팩토링 해보았다!
package section1;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class IndexMaker {
static Item items[] = new Item[100000];
static int n = 0;
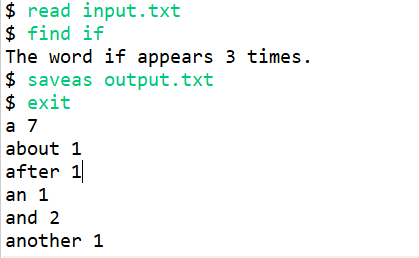
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner kb = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true) {
System.out.print("$ ");
String command = kb.next();
if(command.equals("read")) {
String filename =kb.next();
makeIndex(filename);
}
else if(command.equals("find")) {
String str = kb.next();
int index = findWord(str);
if(index > -1) {
System.out.println("The word " + items[index].word +" appears " + items[index].count + " times.");
}
else
System.out.println("The word " + str +" dose not appears ");
}
else if(command.equals("saveas")) {
String filename = kb.next();
saveAs(filename);
}
else if(command.equals("exit")) {
break;
}
}
kb.close();
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
System.out.println(items[i].word+" "+items[i].count);
}
}
static void makeIndex(String filename){
try {
Scanner inFile = new Scanner(new File(filename));
while(inFile.hasNext()) {
String str = inFile.next();
String trimed = triming(str);
if(trimed != null) {
String t = trimed.toLowerCase();
addWord(t);
}
}
inFile.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.print("No File");
return;
}
}
static String triming(String str) {
int i =0, j = str.length()-1;
while(i <str.length() && !Character.isLetter(str.charAt(i)))
i++;
while(j<str.length() && !Character.isLetter(str.charAt(j)))
j--;
if(i>j)
return null;
return str.substring(i,j+1);
}
static void addWord(String str) {
int index = findWord(str);
if(index != -1) {
items[index].count++;
}
else {
int i =n-1;
for(;i>=0 && items[i].word.compareToIgnoreCase(str)>0;i--) {
items[i+1] = items[i];
i--;
}
items[i+1] = new Item();
items[i+1].word = str;
items[i+1].count =1;
n++;
}
}
static int findWord(String str) {
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
if(items[i].word.equalsIgnoreCase(str)) {
return i;
}
return -1;
}
static void saveAs(String fileName) {
try {
PrintWriter outFile = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter(fileName));
for(int i =0;i<n;i++) {
outFile.println(items[i].word + " " + items[i].count);
}
outFile.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("save failed");
return;
}
}
}
중요한 것은 역시 객체안에 내용을 건들때는 항상new를 통해 생성을 해주어야한다는 것을
자꾸 까먹게 되니 계속 생각을 해야하는것 같다!
'알고리즘 with 자바 > 자료구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 클래스 ,객체, 참조변수 5 (0) | 2021.06.23 |
|---|---|
| 클래스, 객체, 참조변수 4 (0) | 2021.06.22 |
| 클래스, 객체, 참조변수 2 (0) | 2021.06.21 |
| 클래스 , 객체, 참조변수 1 (0) | 2021.06.21 |
| 문자열 다루기 2 (0) | 2021.06.19 |